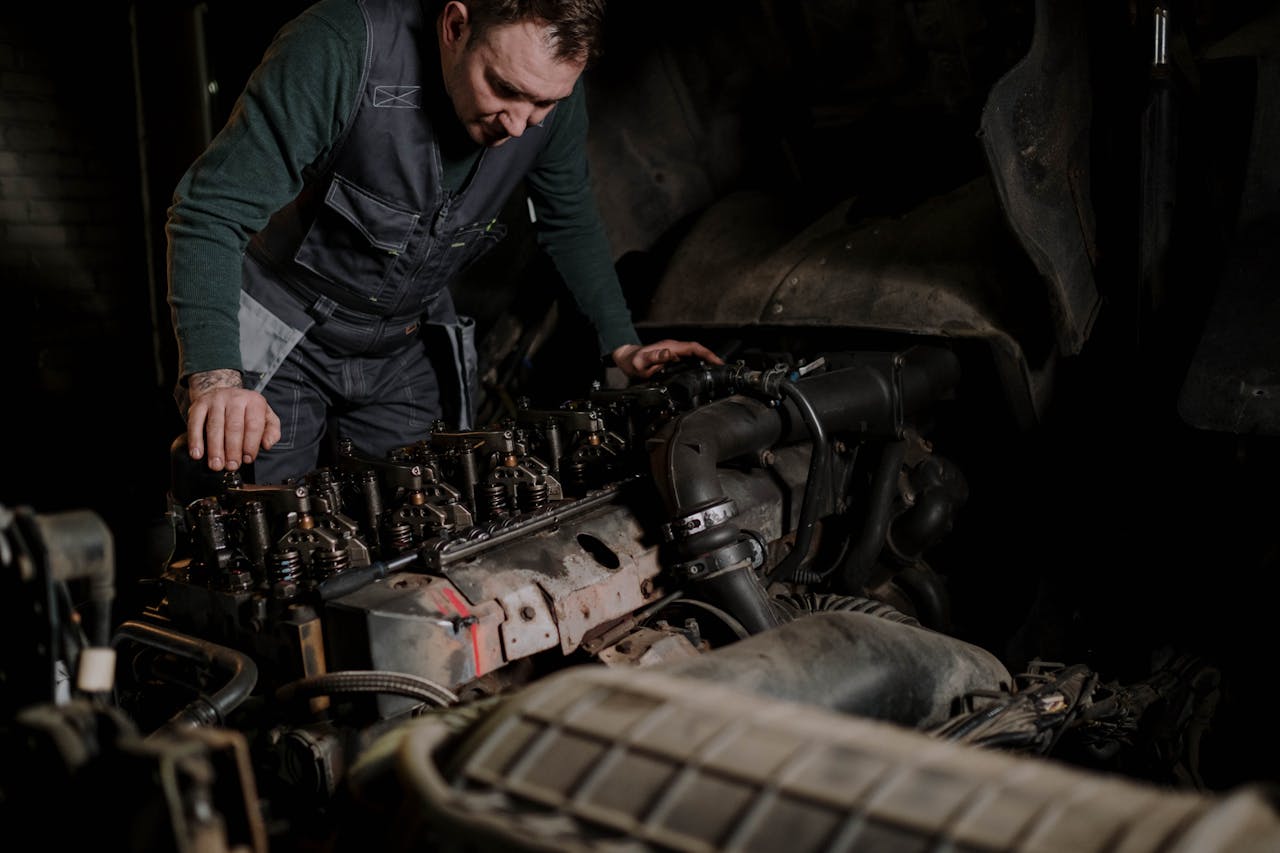
Diesel engines have become renowned for their efficiency, power, and durability. Understanding the mechanics behind these powerful machines equips vehicle owners with essential know-how to properly operate and maintain them. In this guide, we’ll answer some of the common questions asked by diesel car owners:
- How does a diesel engine work?
- How is this engine different from a gas engine?
- What are its advantages and disadvantages?
- What are the various applications of this engine type?
What is a Diesel Engine?
A diesel engine is an internal combustion engine that operates using diesel fuel. Invented by Rudolf Diesel in 1897, this engine type relies on compression ignition, where air is compressed to a high temperature to ignite the fuel. Diesel engines are characterized by their ability to deliver high torque at low RPMs, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications.
How Does a Diesel Engine Work?
In order to understand how a diesel engine works, it's essential to familiarize ourselves with its key components:
- Engine Block: The primary structure that houses various engine parts.
- Cylinder Head: Contains the combustion chamber and houses valves and injectors.
- Pistons: Move within the cylinders to convert energy from combustion into mechanical power.
- Crankshaft: Transforms linear motion from the pistons into rotational motion.
- Fuel Injectors: Atomize diesel fuel and inject it into the combustion chamber.
- Turbocharger and Intercooler: Increase engine efficiency by forcing more air into the cylinders.
Part of knowing how a diesel engine works involves becoming familiar with how its engine cycle occurs:
The operation of a diesel engine follows a four-stroke cycle:
- Intake Stroke: The intake valve opens, and air is drawn into the cylinder.
- Compression Stroke: The piston moves upward, compressing the air to a high temperature.
- Power Stroke: As the piston reaches the top, diesel fuel is injected. The high temperature ignites the fuel, causing an explosion that drives the piston down.
- Exhaust Stroke: The exhaust valve opens, allowing the combustion gasses to exit.
The combustion process in a diesel engine is crucial to its efficiency. Unlike gasoline engines, which rely on spark plugs, diesel engines ignite fuel through compression. The high temperature during the compression stroke ensures the diesel fuel ignites rapidly, releasing energy and driving the piston.
What's the Difference Between a Gas and Diesel Engine?
Understanding the distinctions between gas and diesel engines is vital for appreciating the advantages of diesel technology. Consider the following features:
- Fuel Type: Diesel engines use diesel fuel, which is denser and contains more energy than gasoline. This difference contributes to the higher efficiency of diesel engines.
- Combustion Process: compression ignition. This fundamental difference affects how the engines operate and their overall efficiency.
- Efficiency and Power Output: Diesel engines are generally more efficient than gas engines, providing greater torque and better fuel economy. The ability to generate higher torque at lower RPMs makes diesel engines suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Maintenance and Longevity: Diesel engines are built for durability and often have longer lifespans than their gasoline counterparts, provided they receive proper maintenance.
How is a Diesel Engine Efficient?
Your car’s diesel engine is designed with various efficiencies in mind, including fuel, thermodynamics, RPM torque, and engine design.
Thermodynamic Efficiency
Diesel engines boast higher thermal efficiency than gasoline engines. Their higher compression ratio allows for more complete combustion and energy extraction from the fuel.
Fuel Efficiency
Diesel engines are known for their exceptional fuel economy, often delivering 20-30% more miles per gallon than gasoline engines. This efficiency is due in part to the energy density of diesel fuel.
Low RPM Torque
The high torque generated at low RPMs allows diesel engines to perform well under heavy loads, making them ideal for trucks and industrial applications.
Engine Design Innovations
Recent advancements in diesel engine technology have further improved their efficiency. Innovations such as common rail direct fuel injection and turbocharging enhance performance while reducing emissions.
How is Diesel Fuel Different?
Diesel fuel differs significantly from gasoline in its chemical composition. It is composed of longer hydrocarbon chains, which contribute to its higher energy density. In addition, the cetane rating of diesel fuel measures its ignition quality. Higher cetane numbers indicate better ignition properties, leading to smoother operation and reduced emissions.
Further, diesel engines emit lower amounts of carbon dioxide than gasoline engines, but can produce higher levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter. However, modern diesel engines are equipped with technologies to mitigate these emissions.
The Pros and Cons of Diesel Engines
Whether you're considering purchasing a diesel-powered vehicle or simply curious about how these engines differ from their gasoline counterparts, it's important to weigh both the advantages and drawbacks:
Advantages
- Diesel engines provide superior fuel efficiency.
- The high torque output makes diesel engines ideal for towing and hauling heavy loads.
- Diesel engines are built to last, often outliving gasoline engines with proper care.
Disadvantages
- Diesel engines can have a higher initial cost.
- They tend to be noisier and produce more vibrations compared to gasoline engines.
- Although advancements have been made, diesel engines still face scrutiny regarding NOx and particulate emissions.
What Vehicles Use Diesel Engines?
Diesel engines are here to stay, given their efficiency and durability. Here are some of the most common applications and use cases of this engine type:
Common Applications
Diesel engines are widely used in various vehicles, including:
- Heavy-Duty Trucks: Diesel engines are preferred for long-haul trucking due to their efficiency and power.
- Buses: Public transportation systems frequently use diesel buses for their reliability.
- Agricultural Machinery: Diesel engines power tractors and other farming equipment, providing the necessary torque for demanding tasks.
- Marine Applications: Many boats and ships rely on diesel engines for fuel efficiency and robustness.
Emerging Applications
In recent years, diesel engines have gained traction in passenger vehicles and light-duty trucks. Current innovations in diesel technology, like those from the New European Driving Cycle (NEDC), are also being explored in hybrid and electric vehicle systems, showcasing the adaptability of diesel engines.
Get Top-Notch Diesel Engine Service in the DFW Area
Understanding how a diesel engine works is crucial for anyone operating or maintaining these powerful machines. Regular maintenance keeps your engine in top condition.
If you are looking for premier diesel engine maintenance and repair services, look no further than Big Shop Diesel Services. Our experienced technicians provide comprehensive maintenance and repair services to prevent unexpected breakdowns and prolong your engine’s life.
Experience the best in diesel engine maintenance. Call 817-473-8565 today to book your appointment.